

Hair Color Basics
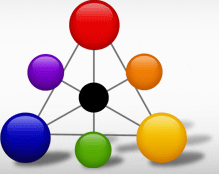
Your hair is a mixture of 3 colors; red, yellow, and blue. These are the primary colors. Secondary colors are orange, green, and violet. If you look at the "wheel" a color opposite (directly across) will "negate" that color
If you know the color wheel color becomes easy. It may sound a bit odd but your hair is a mixture of 3 colors; red, yellow, and blue. These are the primary colors. Secondary colors are orange, green, and violet. If you look at the "wheel" a color opposite (directly across) will "negate" that color. This means if your hair is a orange color - blue will make it a brown/black color. If you hair has a yellow tone, violet will cancel it out.
One of the most important elements of haircoloring is determining the hairs' "underlying pigmet" (the hairs' natural color.) When you chose a color in a swatch book, your hair may not come out that color because of the underlying pigment in your hair.
Underlying color + Artificial color = Final result
Levels of Hair Color
1=Black
2=Very Dark Brown
3=Dark Brown
4=Brown
5=Medium Brown
6=Light Brown
7=Dark Blonde
8=Light Blonde
9=Very Light Blonde
10=Light Platium Blonde
How it Works:
Before any permanent color can be deposited into the hair shaft, the cuticle, or outer layer, must be opened.
The insoluble formula then reacts with the cortex, or middle layer, to deposit or remove the color. The color is available in a variety of forms; creams, gels or tubes, or shampoos.
These will not permanently change the hair color until they are part of an oxidation chemical reaction.
The Oxidizing Agent or Developer is hydrogen peroxide in one of various forms and strengths. lt is the catalyst or cause of the chemical reaction which allows the formula to permanently alter the hair's color. The strength of the developer - is determined by the desired results directions.
Too much developer and the color may not have good highlights, cover poorly, not lift to the correct level and fade more quickly.